

This report aims to promote the incorporation of sustainability and climate resilience into investment principles and policies of the Asian Infrastructure Development Bank (AIIB), a multilateral development banks co-led by China, which could help capital markets allocate more resources to environmentally friendly, climate-resilient and low-carbon infrastructure investments. The report evaluated whether the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank has lived up to its promise to be ‘Lean, Clean and Green’ by analyzing the alignment with Paris Agreement and SDGs of AIIB’s environmental and social related strategies and policies, and project implementations.

In order to reduce and avoid social and financial risks arising from environmental factors in China’s overseas investment , and guide domestic institutions to follow the Principles for Responsible Investment, further greening the BRI by fully integrating the notion of ecological civilization and low-carbon into the implementation,and contribute to achieving United Nations 2030 Sustainable Development Goals and goals of Paris Agreement, the Green Finance Committee of Finance Association of China (hereinafter referred to as the Green Finance Committee) established the Task Force on Environmental Risk Management for China’s Overseas Investment in 2017, a move under Environmental Risk Management Initiative for China’s Overseas Investment jointly launched by seven associations and committees subordinated to ministries. Subsequently, Environmental Risk Management Manual for China’s Overseas Investment (hereinafter referred to as the “Manual”) was finalized by the Task Force and was issued at the International Green Finance Forum hosted by Green Finance Committee in April 2018.Authored by GHub and supported by Heinrich-Böll-Stiftung, this report, as the main part of the Manual, mainly includes the objective, scope and general guidelines for environmental risk management of China’s overseas investment, typical environmental risk identification and assessment cases of BRI countries, country-specific climate risk management cases, as well as international conventions, industry norms and national laws and regulations.

In recent years, marine protection has gradually become a hot topic in international environmental politics. MPA, as a tool of marine zoning management, has attracted more and more concern and attention. In this context, a seminar on “Design of Large Marine Protected Areas: Theory and Practice” was held on August 27, 2018 by G-Hub and the International Master of Environmental Policy Program of Duke University and Duke Kunshan University. The seminar shared the case study of Antarctic and Yellow Sea ecosystems, and considering the background of climate change, the principles, methods and practices of the construction of large-scale MPAs were discussed. G-hub has complied the report based on the presentations, hoping to promote the learning and exchange among those concerned about marine protection in China.
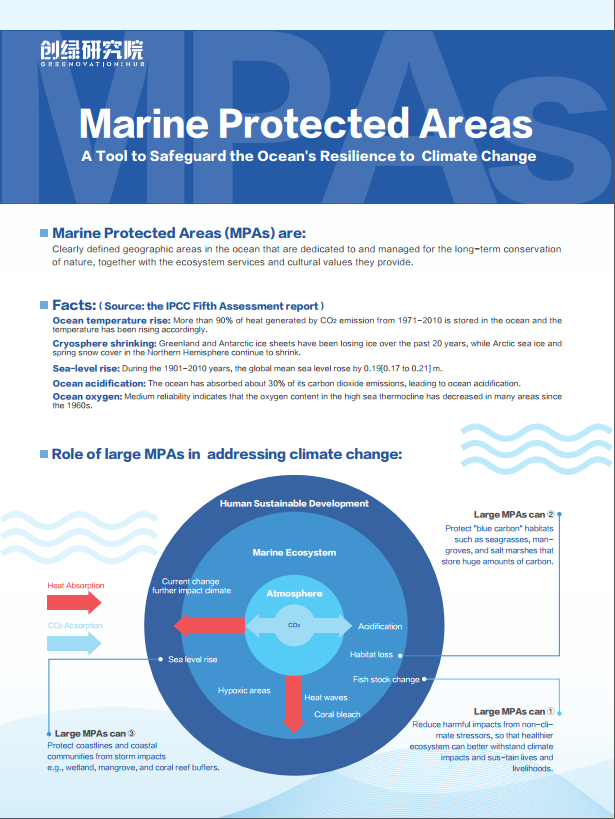
Large marine protected areas (MPAs) can protect the ocean’s resilience more effectively and play an essential role in supporting climate change adaptation and mitigation.

The term “discourse power” is generally considered to originate from Foucault’s “Discourse is power”. The particularity of the global commons has meant that only a few countries were able to participate substantively in decision-making, which is sometimes in the name of “representing all humanity” So, the moral factor really matters in the mainstream discourse when it comes to problems in the public common. Therefore, it is crucial to coordinate national interests with the interests of all mankind in mind, and also short-term interests with long-term interests in public common. This paper observes a specific negotiation process on environmental protection which is a common issue, and proposes a framework for analyzing the institutional discourse power in common governance for discussion, and attempts to put forward some practical recommendations.
The Paris Agreement, which came into force in 2016, sets a long-term goal of decarbonizing the global economy to protect vulnerable people from extreme weather and other weather-induced events. The “Belt and Road Initiative” aims to build a “green, intellectual, and peaceful” Silk Road, and proposes to strengthen green and low-carbon infrastructure construction and operation, with consideration on the impact of climate change in construction. Based on the international green investments in power sector, this paper identifies the potential risks and new opportunities facing China’s power investment in key Asian countries, while considering their national independent contributions and power development plans. It also provides reference and recommendations for Chinese policy makers and investors in developing power investment plans along “ Belt and Road” that are consistent with the 2°C temperature objectives of the Agreement.